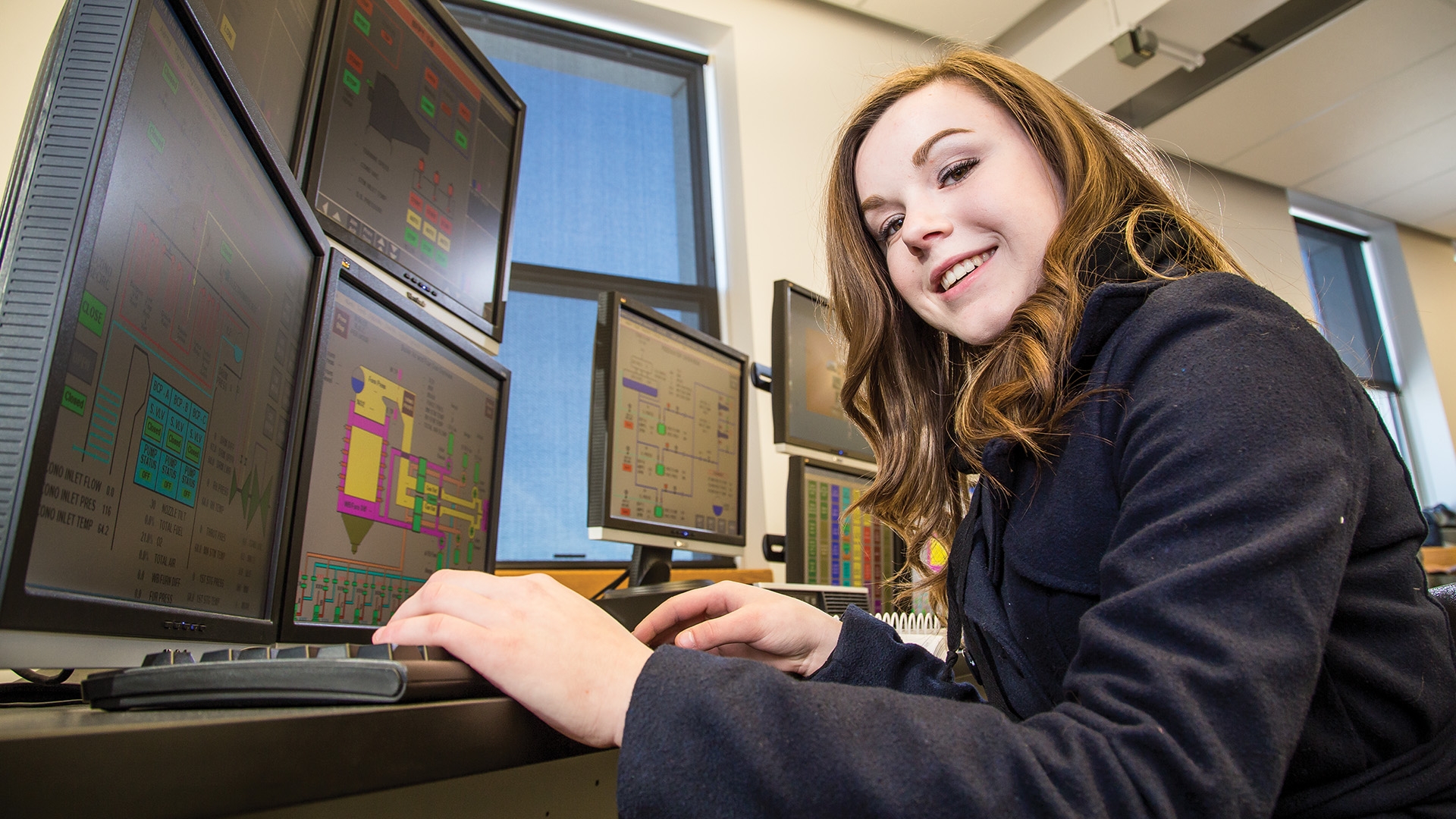
Power Engineering
Overview
Assiniboine’s two-year Power Engineering diploma program prepares graduates in the design, operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of power plants and energy production systems.
Power engineers work in various industries, including chemical manufacturing, food processing and electrical generation. They may work in buildings or institutional complexes like hospitals, government agencies, school divisions, regional health authorities and manufacturing plants - anywhere that maintains complex mechanical systems.
This program prepares you to write the certification examinations for 4th Class and 3rd Class Power Engineering.
Program Learning Outcomes
- Complete work in compliance with provincial and/or national codes, applicable laws, standards and ethical practices in industry.
- Comply with health and safety practices and procedures in accordance with current legislation and regulations
- Operate automated or computerized control systems, stationary engines and auxiliary equipment such as reactors, boilers, turbines, generators, pumps, compressors, pollution control devices and other equipment to generate electrical power and to provide light, heat, ventilation and refrigeration for buildings, industrial plants and other work sites.
- Start up and shut down power plant equipment, control switching operations, regulate water levels and communicate with systems operators to regulate and coordinate transmission loads, frequency and line voltages.
- Monitor and inspect plant equipment, computer terminals, switches, valves, gauges, alarms, meters and other instruments to measure temperature, pressure and fuel flow to detect leaks or other equipment malfunctions and to ensure plant equipment is operating at maximum efficiency.
- Analyze and record instrument readings and equipment malfunctions
- Troubleshoot and perform corrective action and minor repairs to prevent equipment or system failure
- Communicate and collaborate with diverse clients, supervisors, coworkers and tradespersons to complete projects on time and to maintain effective working relationships.
Examples of what power engineers can do:
- Operate and repair equipment and machinery found in industrial settings.
- Clean and lubricate generators, turbines, pumps and compressors and perform other routine equipment maintenance duties using appropriate lubricants and hand, power and precision tools.
- Use specialized instrumentation and equipment.
- Maintain a daily log of operation, maintenance and safety activities, and write reports on plant operation and non-compliance.
- May assist in the development of operation, maintenance and safety procedures.
Success Factors
You might be a good fit for this program if you have or would enjoy:
- An interest and strong technical aptitude for understanding complex energy production systems and how they work.
- Be meticulous and pay close attention to detail to ensure that power plants and energy production systems are operating efficiently and safely.
- Analyze data, diagnose problems, and develop effective solutions quickly and efficiently.
- Able to communicate effectively with clients, contractors, and other workers to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
- Prioritize safety and follow appropriate safety procedures to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Able to adapt to changing situations and work effectively in a variety of settings.
- Working independently or in small teams, so power engineers must be self-motivated and able to stay on task without direct supervision.
- Continually learning and adapting to changing conditions and technological advancements in the field.
A valid driver’s license and access to a vehicle is strongly recommended given the potential need to travel for practicum placement.
The industry and program environment require individuals to:
- Be reliable, punctual, and regularly attend.
- Move around and work within the learning environment, negotiating different areas including stairs and ladders, confined spaces, heights, uneven terrain and scaffolds.
- Complete responsibilities requiring standing, bending, and climbing.
- Have the strength, dexterity, balance and stamina required to work in or on equipment.
- Work in noisy, dusty and/or fumes areas with appropriate personal protective equipment.
- Interpret technical documents, drawings, specifications, codes, regulations, bylaws and standards.
- Communicate effectively with others including suppliers, co-workers, other trades people, safety and building inspectors, manufacturer representatives, and customers.
- Work in industry-specific shifts, schedules, and conditions.
- Listen to direction and act on that accordingly.
- Demonstrate safety-conscious attitudes and work practices.
Admissions
Admission Requirements
- A complete Manitoba Grade 12 or equivalent
- English 40G/40S or equivalent
- Pre-Calculus or Applied Mathematics 40S or equivalent
- Physics 30S or Chemistry 30S or equivalent
If you received your education outside of Manitoba, please review the equivalent admission requirements: Interprovincial or International.
English is the language of instruction at Assiniboine. All applicants educated outside of Canada or in a country not on the test exempt list are expected to meet the English language proficiency requirements.
READY TO TAKE THE NEXT STEP IN YOUR EDUCATION JOURNEY?
Start your online application today and join Assiniboine College!
Eligible applicants, with a current 4th Class Power Engineers Certificate (licensed through the authority having jurisdiction), may apply for direct entry into year two of the program. Seat availability may vary.
DON'T MEET ADMISSION REQUIREMENTS?
If you don’t meet admission requirements, visit our Centre for Adult Learning to upgrade courses.
Careers & Connections
Career Opportunities
- Water treatment plants
- Hospitals
- Government agencies
- School divisions
- Production plants
- Building complexes
Connections
Graduates may write the Standardized Power Engineering Examinations. Candidates who pass these examinations receive a Standardized Certificate, which makes them eligible to work as power engineers in all Canadian provinces and territories except Quebec.
Assiniboine has a number of agreements with other colleges, universities and professional organizations, making it possible to apply credit taken at Assiniboine to programs at other institutions. For information on agreements, see Articulation Agreements.
Tools & Supplies
Students have the opportunity to operate a real-life power plant using a state of the art simulator. This equipment simulates a 400 MW, pulverized coal-fired steam generating unit.
Our classrooms and labs are equipped with the necessary equipment that you need to make the most of your experience. However, there are some tools and supplies that you will need to purchase for personal use to help you with your studies. Much of what you purchase you’ll be able to use after you graduate and begin your career.
Program Checklists, Textbooks, and Supplies
ASSINIBOINE BOOKSTORE
Textbooks, supplies and uniforms may be purchased at the Assiniboine Bookstore at the Victoria Avenue East Campus. Booklists are available from your school office 30 days prior to the start date of your program.
Technology Requirements
Students in this program are expected to have a computer at home with internet access that meets the technical needs outlined by the program. For more details, see At-Home Computing.
Courses & Costs
Costs
Estimated Program Costs
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Credits | 66.0 | 66.0 |
| Tuition | $4,090 | $4,020 |
| Course Fees | $1,950 | $2,040 |
| Students' Association fees (including Health Premium) | $610 | $600 |
| Estimated textbooks, tools, and supplies | $3,870 | $2,670 |
All fees are estimated and subject to change without notice.
For more information, visit the Fees and Charges page.
Courses
To graduate with a Power Engineering diploma, students must successfully complete 120 academic credits and 12 practical credits. To graduate with a Power Engineering certificate, students must successfully complete 60 academic credits and 6 practical credits. The minimum passing grade for each course is indicated on the course outline. Course offerings are subject to change and may vary by intake.
Year One Courses
| Title | Credits/CEUs | Elective | Distance | PLAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Blueprint Reading (PE) (DRFT-0005)This course provides the fundamental skills required to read and interpret blueprints and drawings. The knowledge gained in this course will prepare the student to better communicate ideas and proposed equipment changes for real situations in industry. This course includes lettering, description of lines and weights, orthographic and isometric views, sectional views and freehand sketching. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Boilers and Materials (ENGR-0030)This course introduces the student to various types of boiler designs, including where they are used, their history, construction and applications in both commercial and industrial settings. The student will also learn about the mechanical properties of ferrous and non-ferrous materials including piping, piping components, and valves. Welding of these materials will also be discussed. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
College Foundations (PEDV-0356)This course improves students' ability to navigate the college experience and environment, including student's rights, roles, and responsibilities. In this course, students reflect on their skills, attitudes, and expectations and develop learning strategies to help them to become successful, resilient, and self-directed learners. The course covers topics such as success in online learning, time management strategies, learning strategies, assessment taking strategies, academic integrity, information and digital literacy, and wellness, among others. It integrates elements of student orientation. |
0 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Combustion and Maintenance 1 (ENGR-0046)This course introduces students to different types of fuels used to fire boilers and how these fuels are utilized. Students will learn the different applications and techniques used to achieve proper combustion. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Combustion and Maintenance 2 (ENGR-0047)Prerequisite: ENGR-0046 Combustion and Maintenance 1 |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Communications (COMM-0045)This course includes instruction in techniques to improve both written and oral communication with prospective employers, co-workers and clients. Effective strategies for customer service are emphasized. It also serves to familiarize students with the regulations related to the workplace. As well, students receive an introduction to the use of computer software and hands-on experience with Windows operating system, Internet and email. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Electrical 1 (PE) (ELEC-0025)This is an introductory course to help students become conversant with electrical terms and applied electrical principles, concepts and relationships that are fundamental to many technical applications. The course covers current and voltage relationships, terminology associated with alternating current (AC), direct current (DC) and magnetism. Electrical symbols and the various types of diagrams associated with the production, distribution and operation of electrical components and systems are studied. The course is conceptual while working toward problem solving and applications in industry. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Engineering Chemistry (SCIE-0036)This is an introductory course in water chemistry as it relates to boilers and cooling water systems. Students learn the different methods of treating water both internally and externally of these systems. Students also learn laboratory techniques for water testing. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Engines (PE) (ENGR-0018)This course provides an introduction to steam engines, steam turbines, internal combustion engines and lubrication. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Heating Boilers and Systems (ENGR-0031)Prerequisite: ENGR-0030 Boilers and Materials |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Instrumentation and Controls 1 (ENGR-0048)In this course, students will be able to understand the principles involved for measuring and controlling variables found in power plants. These variables include level, temperature, pressure, flow and composition. The student will become familiar with how these process variables are measured and where the information is used. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Instrumentation and Controls 2 (ENGR-0049)Prerequisite: ENGR-0048 Instrumentation and Controls 1 |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Mathematics (PE) (MATH-0050)This is a skill development course in arithmetic, applied geometry and lower level algebra. Emphasis is on hand-held calculator skills and realistic applications. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Mechanics (PE) (MECH-0083)This is an introductory course on the study of statics and dynamics. This includes friction, types of motion, work, power, energy and some power mechanical transmission. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Practicum 1 - PWRNG (PRAC-0301)Gain valuable on the job training and experience in a power plant work environment. Students must submit evidence that the work practicum has been successfully completed. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Refrigeration (PE) (ENGR-0019)Students can expect to learn about the different types of commercial and industrial refrigeration systems including the use of different types of refrigerants, equipment, applications, safety controls, and the maintenance and operation procedures of each plant. Refrigeration theory along with heat gains and losses will also be discussed. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Safety and Environment (WRKP-0016)This course provides an introduction to safety problems and safe practises in the workplace, and an appreciation of the potential environmental impact of air, water, waste and noise. Some discussion on the handling of waste and perception of risk, environmental responsibility and sustainable development is included. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Thermal and HVAC Studies 1 (ENGR-0050)This course provides students with the skills to solve problems related to thermodynamics. This course covers temperature scales, heat transfer, steam generation, and laws for perfect gases. Density and pressure, temperature and heat, force, pressure, calorimetry, expansion and contraction, and the laws of thermodynamics are also discussed. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Thermal and HVAC Studies 2 (ENGR-0051)Prerequisite: ENGR-0050 Thermal and HVAC Studies 1 |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Year Two Courses
| Title | Credits/CEUs | Elective | Distance | PLAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Advanced Mathematics (PE) (MATH-0118)Prerequisite: MATH-0050 Mathematics (PE) |
4.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Advanced Mechanics (PE) (MECH-0149)Prerequisite: MECH-0083 Mechanics (PE) |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Advanced Thermodynamics (ENGR-0052)Develop your understanding of temperature scales, heat transfer, steam generation, laws for perfect gases, change of state and calorimetry to solve advanced problems related to thermodynamics. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Boiler Design (ENGR-0053)Understand boiler construction methods and various types of boiler designs including where they are used, their history, and applications in both commercial and industrial settings. |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Boiler Systems and Operation (ENGR-0054)Understand the various systems that allow the boiler to operate safely and efficiently, systems include fuel, burner, draft, flue gas, and controls. Learn common operational and maintenance procedures related to boiler equipment. |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Boiler Water Treatment (ENGR-0055)Prerequisite: SCIE-0036 Engineering Chemistry |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Codes and Combustion (ENGR-0056)Learn about legislation and codes for power engineers as well as ASME Section 1 code calculations for power boilers. Develop understanding of the fuels used to fire boilers, how these fuels are utilized, and the different applications and techniques used to achieve proper combustion. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Compressor Principles (ENGR-0057)Discuss the classification, design, and operating principles of industrial air and gas compressors. Learn air compressor auxiliary operation, controls, and operational procedures. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Electrical 2 (PE) (ELEC-0037)Prerequisite: ELEC-0025 Electrical 1 (PE) |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Fuel-Powered Equipment (ENGR-0058)Prerequisite: ENGR-0018 Engines (PE) |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Industrial Safety (WRKP-0077)Learn about a variety of safety programs, best practices and fire safety protocols common in many workplaces. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Industrial Science (SCIE-0089)Develop understanding of the chemical and physical properties of materials from production through the useful life cycle of the material and gain practical understanding of industrial drawings. |
4.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Instrumentation and Controls 3 (ENGR-0059)Prerequisite: ENGR-0049 Instrumentation and Controls 2 |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Piping Design (ENGR-0060)Learn the mechanical properties of ferrous and non-ferrous materials including piping, piping components and valves. Discover how proper design can help mitigate problems, such as water hammer, in the piping system. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Practicum 2 - PWRNG (PRAC-0307)Prerequisite: PRAC-0301 Practicum 1 - PWRNG |
6 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Pump Systems (ENGR-0061)Learn about the design, principles of operation, and maintenance of various pumps. Complete pump calculations based on a variety of pumping systems. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Refrigeration and Heating (ENGR-0062)Prerequisite: ENGR-0019 Refrigeration (PE) |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Steam Turbines (ENGR-0063)Prerequisite: ENGR-0018 Engines (PE) |
3 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Wastewater Treatment (ENGR-0064)Understand the need for, design, processes, and control of wastewater treatment systems. Learn the components of maintenance and administration programs for utilities and process facilities. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Welding and Pressure Vessels (WELD-0062)Discuss various welding techniques used in the construction and repair of equipment used in power plants. Become familiar with the ASME Section 8 code in relation to pressure vessels. |
1.5 credit(s) | No | No | No |
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need protective clothing and/or footwear for Power Engineering?
Yes, students are required to wear CSA approved footwear and safety glasses in all shop/lab classes. Hearing protection and hard hats may be required in certain shop situations. Coveralls may be needed to keep all other clothing clean and protected.
Do I need to buy tools for this program?
Yes, tools are required for this program.
When is the next program information session?
Program information sessions are completely free to attend, and we invite you to bring a guest along as well. It's a good idea to register in advance so we know you're coming.
To find the complete schedule for our program information sessions and to RSVP, visit the program information session page.